PLA Origin
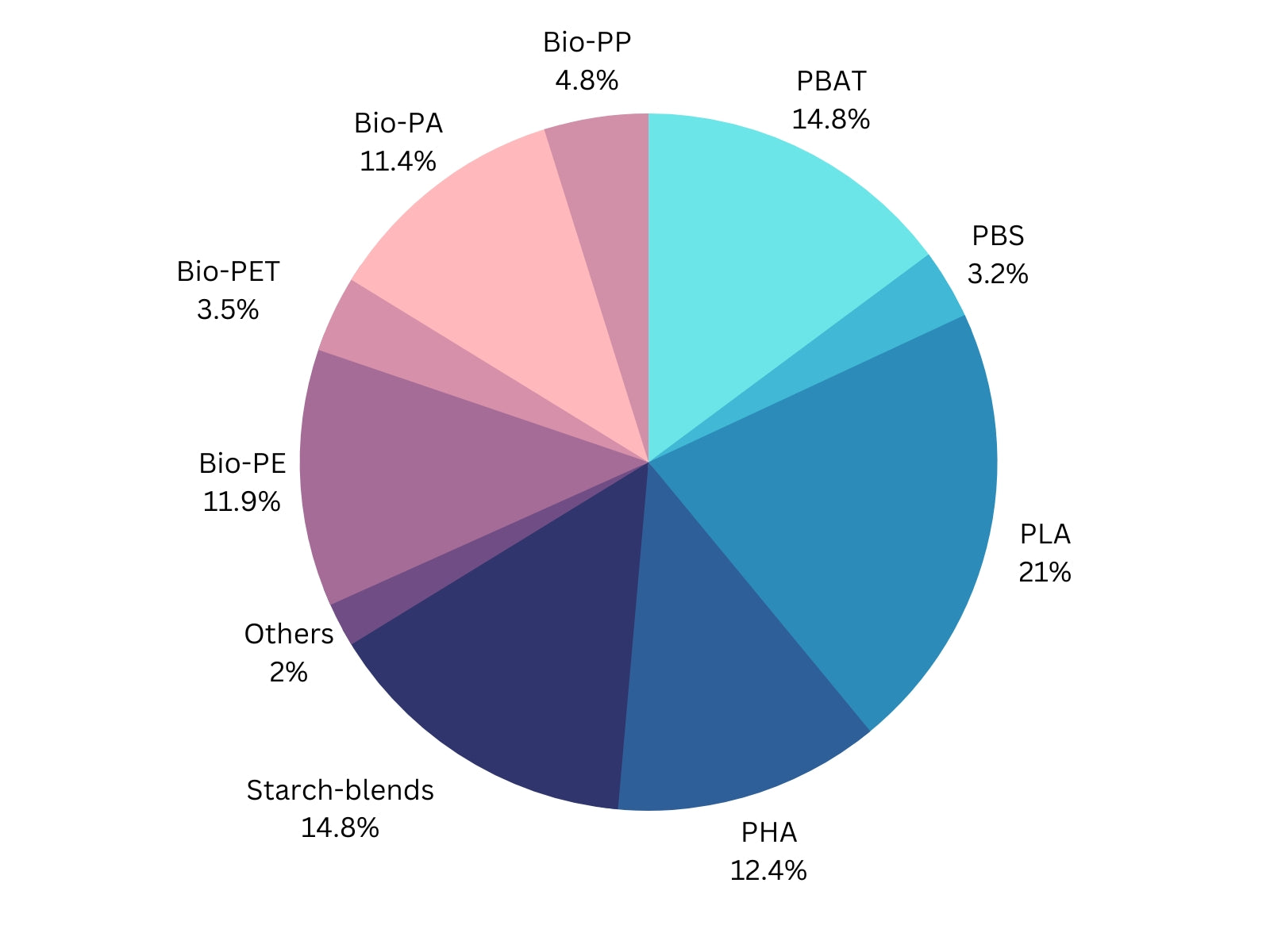
The global PLA market size has been dominating among other bioplastics options. And, packaging industry is the largest consumer of PLA, accounting for over 50% of the total demand.
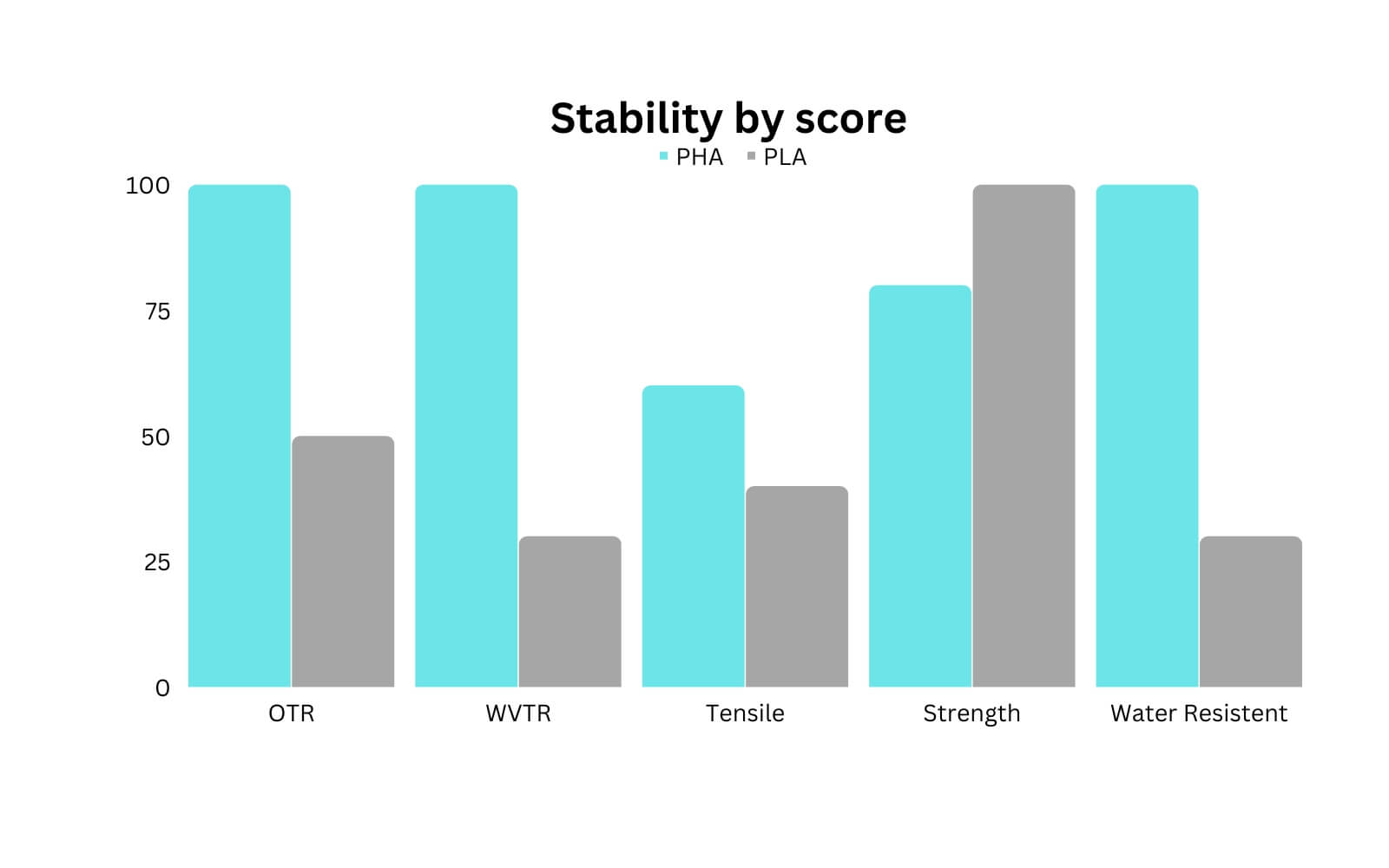
PLA has a relatively low melting point, so it can deform or melt at temperatures around 60-65°C (140-149°F). However, it can withstand higher temperatures for short periods of time, around 80-85°C (176-185°F), without significant degradation. PLA is stable in neutral or slightly acidic environments, but it can degrade in alkaline or highly acidic conditions. It is also susceptible to hydrolysis in the presence of water, which can cause the polymer chains to break down and weaken the material over time. It can degrade over time even without exposure to extreme temperatures or chemicals.
The global PLA market size has been dominating among other bioplastics options. And, packaging industry is the largest consumer of PLA, accounting for over 50% of the total demand.
PLA has a relatively low melting point, so it can deform or melt at temperatures around 60-65°C (140-149°F). However, it can withstand higher temperatures for short periods of time, around 80-85°C (176-185°F), without significant degradation. PLA is stable in neutral or slightly acidic environments, but it can degrade in alkaline or highly acidic conditions. It is also susceptible to hydrolysis in the presence of water, which can cause the polymer chains to break down and weaken the material over time. It can degrade over time even without exposure to extreme temperatures or chemicals.


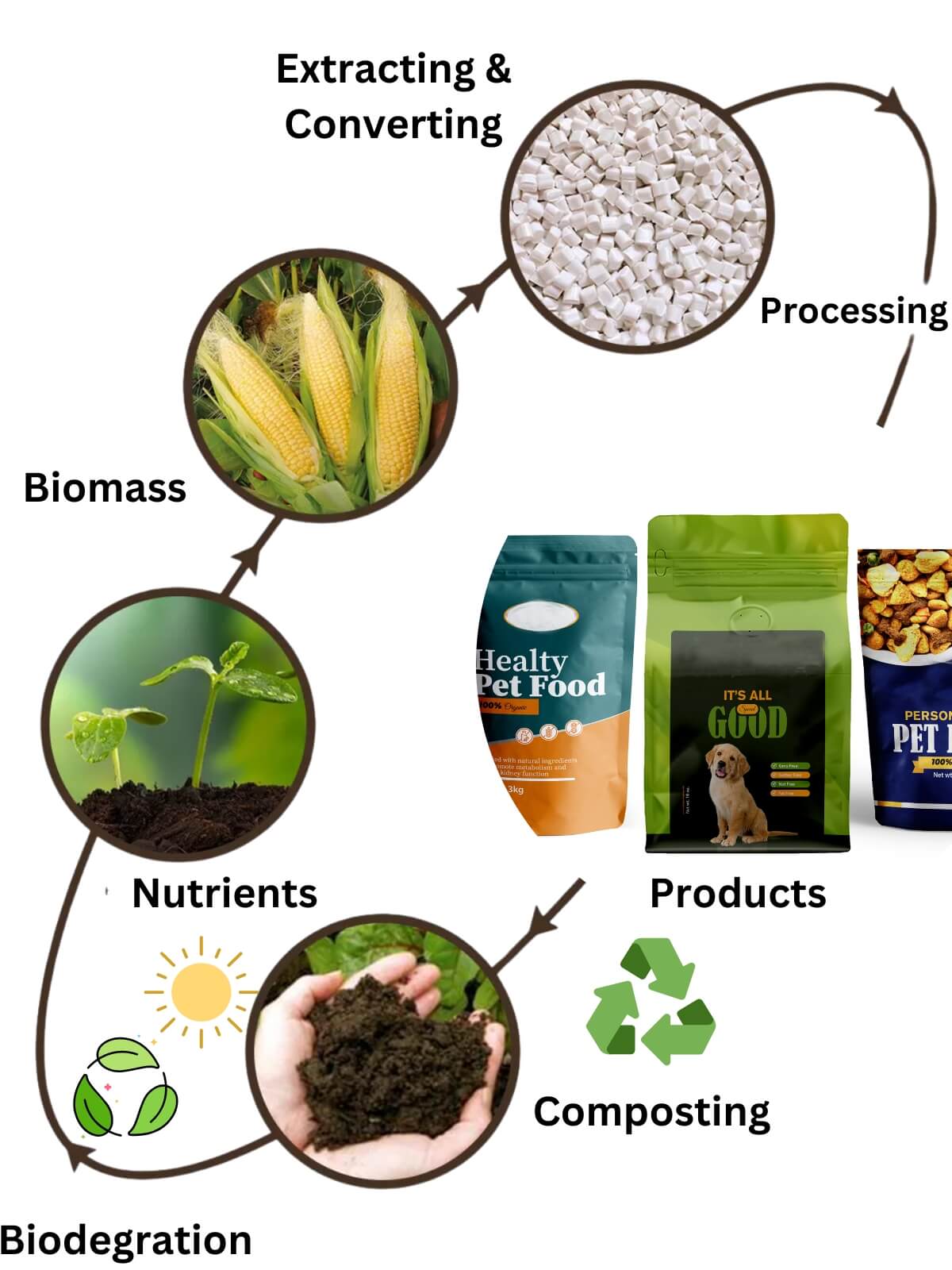
Our compostable plastics lifecycle aligns with the principles of a circular economy. The process begins with the use of biomass raw materials as nutrients for microorganisms. Through fermentation, extraction, downstream processing and other steps, final compostable packaging products are being produced. At the end of the product packaging useage, there will be several options for disposal, including recycling and reuse, composting, and biodegradation. This ensures that the materials used in the production of Anacotte compostable packaging products are recycled and composted with committment: reducing waste and environmental impact.
Compare
PLA properties
Eplore various potential implementations that can be derived from the concept of PLA.
Feature
Properties
Frequent Applications
Bio-baased
Transparency
Food Containers
Flexural strength
Heat Resistance
Degradable Plastics Bags
Tear Strength
Biodegradability
Coating Films
Better Strength
Stronger Barrier
Durable Films and Bags
Better Biodegradability
Robust Decompostability
Composite Materials
Durable, opaque, large compatibility, strong biodegradability
Strong Biodegradability
Multi-purpose
PLA Application in packaging
- Bottle
- Container
- Trays
- Tubes
- Lids
- and more..
- Films
- Bags
- Pouches
- mailers
- and more..






